Beyond Algorithms: The Human Benefits of AI and Automation in Underwriting

The insurance industry is undergoing a technological revolution, and artificial intelligence (AI) combined with automation has been at its forefront. With these advancements, the traditional methods of underwriting are being replaced by smarter, faster, and more accurate processes. This transformation is not just about technology; it’s about redefining how insurers do business, build new products, improve customer experiences, and drive profitability. In this blog, we’ll explore some high level concepts on how AI and automation are streamlining underwriting and what this means for the future of insurance. In order to understand the present and future, let’s examine how underwriting has been done traditionally.
What is Traditional Underwriting?
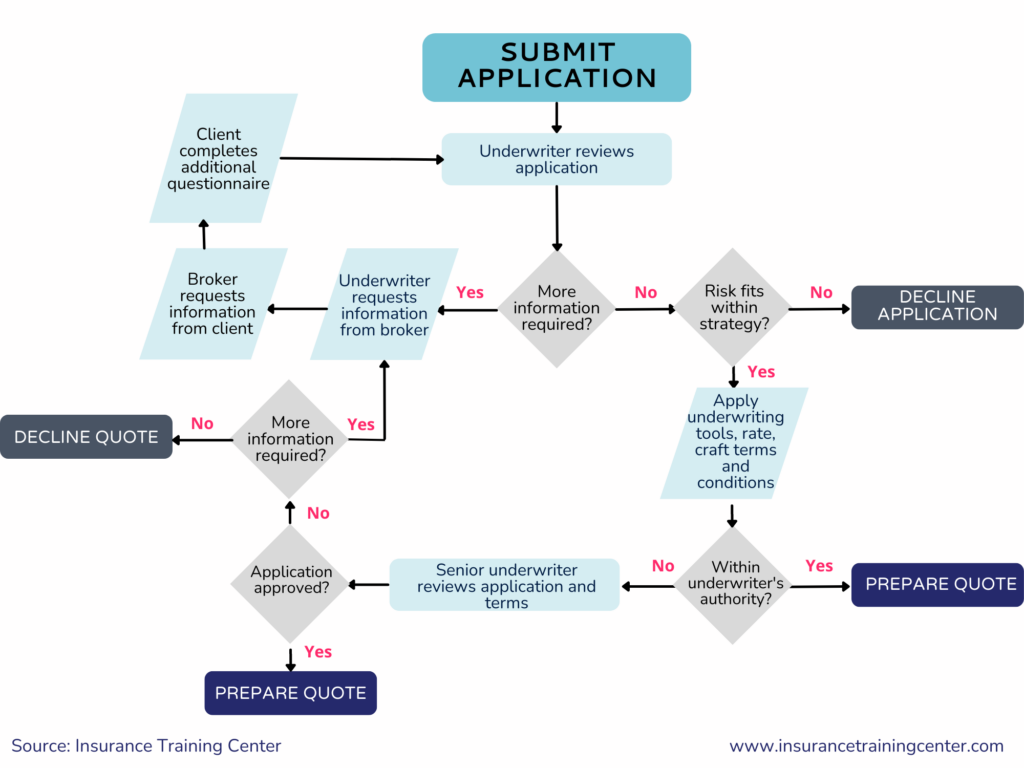
Traditional underwriting is a comprehensive and manual process where underwriters evaluate the risk profile of applicants to determine their eligibility for insurance coverage and to set appropriate premium rates. This process is fundamental across various types of insurance, including life, health, property, and casualty insurance. It involves several key steps and relies heavily on the expertise and judgment of underwriters. Traditionally an underwriter’s daily tasks involved:
-
- reviewing insurance applications,
- collecting and verifying data,
- assessing risks,
- making decisions on approvals and premiums.
They were documenting decisions, preparing reports, and communicating with agents, brokers, and applicants. Continuous learning and adapting to industry changes were crucial, as was collaborating with claims and actuarial departments. Underwriters were ensuring compliance with regulations and ethical standards, all while managing the tedious balance between risk management and profitability for the insurance company.

What Are the Challenges in Traditional Underwriting?
Underwriting is a critical function within the insurance industry, serving as the backbone of risk assessment and pricing. However, traditional underwriting methods are fraught with challenges that hinder efficiency and accuracy. In this section, we delve into the key issues faced by traditional underwriting and why there is an urgent need for a transformation.

Traditional underwriting is highly labor-intensive. Underwriters spend a significant amount of time manually collecting and reviewing data, filling out forms, and verifying information. This manual approach not only slows down the process but also increases the risk of human error. In a world where speed and precision are paramount, such inefficiencies are increasingly unsustainable.

The traditional underwriting process is time-consuming, often taking weeks or even months to complete. This extended turnaround time can frustrate customers who expect quick decisions in today’s fast-paced digital world. Lengthy processing times can also lead to lost business opportunities as potential customers might seek faster alternatives from competitors.

As the volume of insurance applications increases, scaling traditional underwriting processes becomes a significant challenge. Hiring and training new underwriters is both costly and time-consuming. Moreover, during peak periods, the workload can overwhelm existing staff, leading to delays and potential burnout.

Maintaining a large team of underwriters and supporting staff is expensive. The costs associated with training, salaries, and infrastructure add up, impacting the insurer’s bottom line. In an industry where margins can be thin, reducing operational costs is crucial for maintaining profitability.

The risk landscape is continuously evolving with new risks emerging from technological advancements, climate change, and global economic shifts. Traditional underwriting methods struggle to keep pace with these changes, often relying on outdated models and assumptions. This lag in adaptation can result in inadequate risk pricing and exposure to unforeseen liabilities.

Underwriters are often overwhelmed by the sheer volume of data they need to analyze. This data comes from various sources, including medical records, financial statements, and personal histories. Sifting through this information to identify relevant details is a daunting task. Moreover, disparate data formats and unstructured data add to the complexity, making it challenging to derive actionable insights.

Human judgment, while valuable, can lead to inconsistencies in risk assessment. Different underwriters might interpret the same data differently, leading to variations in underwriting decisions. Such inconsistencies can affect pricing accuracy and the overall risk profile of the insurer’s portfolio. This variability undermines the reliability of the underwriting process and can lead to financial imbalances.
Underwriting is a critical function within the insurance industry, serving as the backbone of risk assessment and pricing. However, traditional underwriting methods are fraught with challenges that hinder efficiency and accuracy. In this section, we delve into the key issues faced by traditional underwriting and why there is an urgent need for a transformation.
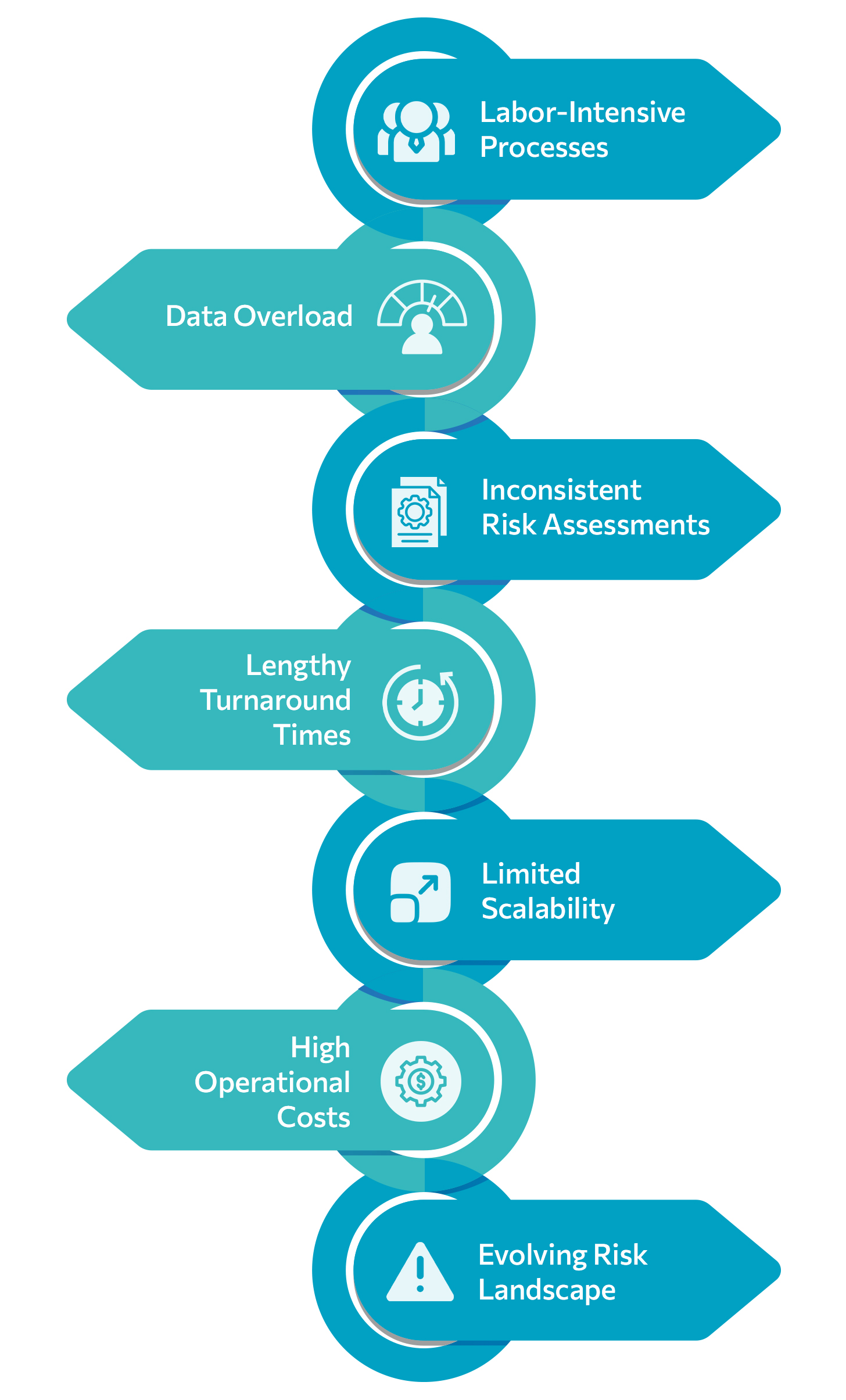
Labor-Intensive Processes: Traditional underwriting is highly labor-intensive. Underwriters spend a significant amount of time manually collecting and reviewing data, filling out forms, and verifying information. This manual approach not only slows down the process but also increases the risk of human error. In a world where speed and precision are paramount, such inefficiencies are increasingly unsustainable.
Data Overload: Underwriters are often overwhelmed by the sheer volume of data they need to analyze. This data comes from various sources, including medical records, financial statements, and personal histories. Sifting through this information to identify relevant details is a daunting task. Moreover, disparate data formats and unstructured data add to the complexity, making it challenging to derive actionable insights.
Inconsistent Risk Assessments: Human judgment, while valuable, can lead to inconsistencies in risk assessment. Different underwriters might interpret the same data differently, leading to variations in underwriting decisions. Such inconsistencies can affect pricing accuracy and the overall risk profile of the insurer’s portfolio. This variability undermines the reliability of the underwriting process and can lead to financial imbalances.
Lengthy Turnaround Times: The traditional underwriting process is time-consuming, often taking weeks or even months to complete. This extended turnaround time can frustrate customers who expect quick decisions in today’s fast-paced digital world. Lengthy processing times can also lead to lost business opportunities as potential customers might seek faster alternatives from competitors.
Limited Scalability: As the volume of insurance applications increases, scaling traditional underwriting processes becomes a significant challenge. Hiring and training new underwriters is both costly and time-consuming. Moreover, during peak periods, the workload can overwhelm existing staff, leading to delays and potential burnout.
High Operational Costs: Maintaining a large team of underwriters and supporting staff is expensive. The costs associated with training, salaries, and infrastructure add up, impacting the insurer’s bottom line. In an industry where margins can be thin, reducing operational costs is crucial for maintaining profitability.
Evolving Risk Landscape: The risk landscape is continuously evolving with new risks emerging from technological advancements, climate change, and global economic shifts. Traditional underwriting methods struggle to keep pace with these changes, often relying on outdated models and assumptions. This lag in adaptation can result in inadequate risk pricing and exposure to unforeseen liabilities.
Conclusion
The challenges faced by traditional underwriting are significant and multifaceted, affecting efficiency, accuracy, and scalability. Addressing these challenges is critical for insurers to remain competitive and meet the demands of the modern market. In the next part, we will explore how AI and automation are revolutionizing underwriting processes to overcome these challenges.